All published articles of this journal are available on ScienceDirect.
Nitro-oxidative Mechanism and Therapeutic Potential in Diabetic Retinopathy
Abstract
The retinal circulation is a specialized system vital for delivering oxygen and nutrients, regulating vascular tone, and maintaining a stable microenvironment for neurons, glia, and blood vessels. In diabetes, chronic hyperglycemia induces oxidative stress, inflammation, and endothelial dysfunction, disrupting retinal microcirculation. This leads to impaired vascular permeability, ischemia, and neovascularization, ultimately causing Diabetic Retinopathy (DR). The most crucial factor in DR involves nitro-oxidative stress, characterized by increased Nitric Oxide (NO) production or altered expression of Nitric Oxide Synthase (NOS) isoforms. These isoforms, critical for vascular homeostasis and blood flow, generate Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS), such as the superoxide anion. ROS reacts with NO to form peroxynitrite, a damaging molecule that modifies tyrosine residues in proteins, causing nitrotyrosine formation, DNA damage, and lipid peroxidation. These processes compromise the blood-optic nerve barrier, exacerbating retinal damage. Emerging therapeutic strategies were aimed to modulate NOS isoforms by enhancing or inhibiting their activity, supplementing cofactors, or reducing oxidative stress. Such approaches showed promise in mitigating DR progression. This review explores the pathophysiological mechanisms underlying DR, focusing on nitro-oxidative pathways, and highlights the therapeutic potential of targeting these mechanisms. Understanding these processes could pave the way for innovative treatments to combat this debilitating condition.
1. INTRODUCTION
The retinal circulation is a highly specialized system responsible for delivering oxygen and nutrients, regulating vascular tone, and maintaining a balanced microenvironment essential for the proper functioning of neurons, glia, and blood vessels [1]. In the context of diabetes, chronic hyperglycaemia induces oxidative stress, inflammation, and endothelial dysfunction, disrupting retinal microcirculation. This disruption contributes to capillary damage, increased vascular permeability, ischemia, and pathological neovascularization, ultimately leading to Diabetic Retinopathy (DR). Although the pathogenesis of DR remains under investigation, key contributors include oxidative and nitrosamine stress, characterized by elevated Nitric Oxide (NO) and superoxide production, altered expression of Nitric Oxide Synthase (NOS) isoforms, and imbalances in endogenous antioxidant defences, all of which contribute to progressive retinal injury [2].
NO plays a crucial role in regulating blood flow and tissue oxygenation, primarily through the activation of soluble guanylate cyclase (sGC) and inhibition of mitochondrial cytochrome c oxidase [3]. In addition, NO exerts cytotoxic effects via immune cells and serves as an endothelial-derived relaxing factor (EDRF). It is synthesized from L-arginine by the action of NOS enzymes through an enzymatic reduction of nitrate [4]. The physiological expression of NOS has been documented in the retinal blood vessels of mice, rats, and pigs [5, 6], with NOS mRNA identified in the retinal vasculature of rodent models [7]. NO has also been detected in various retinal cell types, including neurons, the pigment epithelium, amacrine and ganglion cells, and photoreceptor ellipsoids in both humans and animal models [8, 9]. This broad distribution underscores its essential role in visual function and its involvement in diseases, such as DR and glaucoma, when dysregulated.
In humans, three isoforms of NOS have been characterised: endothelial NOS (eNOS), neuronal NOS (nNOS), and inducible NOS (iNOS) [10, 11]. These isoforms are encoded by distinct genes located on chromosomes 7, 12, and 17, respectively [12]. eNOS is particularly important for regulating retinal blood flow and maintaining vascular homeostasis by reducing vascular resistance, inhibiting platelet aggregation, and preventing smooth muscle proliferation [11]. While nNOS is primarily involved in neurotransmission and synaptic signaling in the retina, iNOS is typically induced by inflammatory stimuli and produces large quantities of NO, which contribute to oxidative damage [5]. Unlike the constitutive and calcium-dependent activity of eNOS and nNOS, iNOS is calcium-independent and expressed predominantly during pathological inflammation [13]. eNOS activity is further modulated by calcium-independent mechanisms, such as phosphorylation at specific serine, threonine, and tyrosine residues [13]. Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) can also activate eNOS via the Akt signaling cascade, a key mechanism for promoting angiogenesis [14]. The role of eNOS in angiogenesis has been demonstrated in several animal models, emphasizing its dual role in both physiological and pathological retinal vascular processes
2. METHODOLOGY
To ensure transparency and scientific rigor, we conducted a narrative review of the literature on nitro-oxidative mechanisms and therapeutic strategies in Diabetic Retinopathy (DR). A comprehensive literature search was performed using PubMed, Scopus, and Web of Science databases up to May 2025. Search terms included combinations of the following keywords: “diabetic retinopathy,” “nitric oxide,” “nitric oxide synthase,” “oxidative stress,” “nitrosamine stress,” “retinal vasculature,” and “therapeutic targets.” Boolean operators (AND/OR) were applied to optimize search sensitivity and specificity.
We included original research articles, reviews, and clinical studies published in English that directly addressed the role of NOS isoforms, oxidative/nitrosamine stress pathways, and related therapeutic interventions in DR. Articles were screened based on titles and abstracts, and full texts were reviewed to assess eligibility. Studies lacking relevance to retinal pathophysiology or nitric oxide signaling were excluded.
Selected studies were analyzed qualitatively, with a focus on mechanistic insights, preclinical or clinical relevance, and therapeutic outcomes. The findings were then synthesized into thematic sections that highlight biological mechanisms, pathophysiological relevance, and emerging therapeutic approaches. Given the narrative nature of this work, no meta-analytical techniques were employed.
2.1. Pathophysiological Effect of NO and NOS in Retinal Vascular Health
VEGF-induced permeability and endothelial precursor cell mobilization are significantly impaired in eNOS-deficient mice, suggesting a crucial role for eNOS in vascular development [15]. However, its exact function in retinal vascular development remains unclear. Min Ha et al. demonstrated that eNOS deficiency in mice results in growth retardation and delayed retinal vessel development, with reduced tip cell numbers and impaired endothelial proliferation [13]. These findings highlight eNOS as vital for endothelial cell function and blood vessel maturation during retinal angiogenesis. All three NOS isoforms (eNOS, nNOS, and iNOS) operate as homodimers, catalyzing the oxidation of L-arginine to produce NO, using molecular oxygen and NADPH as essential substrates (Fig. 1) [16]. L-arginine availability, regulated by arginine-metabolizing enzymes like arginase 1 and 2, and specific transporters for arginine uptake, is critical for NO synthesis and its downstream effects [17].
NOS isoforms require prosthetic groups, including heme iron along with tetrahydrobiopterin (BH4) as a cofactor, to stabilize their dimeric structure and facilitate electron transfer during catalysis [10, 18]. BH4 deficiency causes eNOS “uncoupling,” resulting in the production of superoxide instead of NO, which contributes to oxidative stress and vascular dysfunction [19]. Hypoxia-induced BH4 depletion disrupts eNOS activity, leading to increased superoxide generation and exacerbating vascular damage, such as vasoobliteration [20]. Conversely, eNOS supports angiogenesis and vascular recovery, underscoring its dual role in retinal vascular diseases. NO also activates soluble guanylate cyclase (sGC), binding to its heme domain and enhancing its catalytic activity [18]. This activation converts guanosine triphosphate (GTP) into cyclic guanosine monophosphate (cGMP), a messenger involved in vasodilation and platelet aggregation inhibition [21]. The NO-sGC-cGMP pathway plays a crucial role in maintaining vascular homeostasis.
Furthermore, NO plays an essential role in the vasodilatory mechanisms of retinal blood vessels. Studies have highlighted the involvement of cyclooxygenase (COX) metabolites in endothelium- and NO-dependent vasodilation within ocular vasculature [22]. In vivo research on rat retinal vessels suggests that NO-mediated vasodilation involves the COX-1–prostacyclin (PGI2)–IP receptor pathway through cAMP signaling [23]. These findings indicate that NO facilitates vasodilation in retinal blood vessels via dual mechanisms: the sGC/cGMP and COX-dependent pathways, demonstrating its multifaceted regulatory role in retinal vascular function. Additionally, iNOS has been implicated in cholinergic vasodilation within the rat retina. Berra et al. demonstrated that amino guanidine, an iNOS inhibitor, significantly attenuated vasodilation induced by carbachol, a cholinergic agonist [24]. This response was mediated by M1 and M3 muscarinic acetylcholine receptors, which were expressed on retinal blood vessels and promoted NO release via iNOS activation.
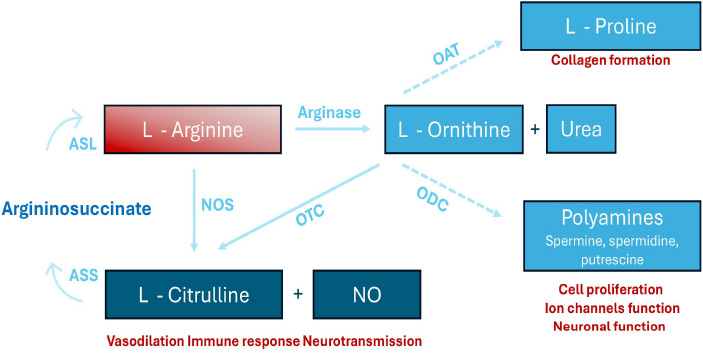
A diagram rof L-arginine metabolism. L-arginine undergoes conversion to L-ornithine and urea via arginase. Additionally, it is metabolized by nitric oxide synthase (NOS) to produce L-citrulline and nitric oxide (NO). The concept was taken from the following source: Shosha E, Fouda AY, Narayanan SP, Caldwell RW, Caldwell RB. Is the Arginase Pathway a Novel Therapeutic Avenue for Diabetic Retinopathy? J Clin Med. 2020 Feb 5;9(2):425.
These findings suggest that iNOS contributes to cholinergic signaling pathways, playing a crucial role in regulating retinal blood flow. Together, these studies expand the understanding of NO’s involvement in both endothelium- and cholinergic-mediated vascular modulation in the retina.
2.2. Nitro-oxidative Stress and Retinal Diseases
Nitro-oxidative stress is a critical pathogenic factor in numerous retinal diseases, affecting both neurons and retinal cells [25]. It involves various contributors, notably NOS and the nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate oxidase (NOX) enzyme family. NOX enzymes consist of seven isoforms (NOX1–5 and DUOX1–2), which facilitate the transfer of electrons from NADPH to molecular oxygen, producing superoxide [26, 27]. Specific isoforms, including NOX1, NOX2, and NOX4, are particularly implicated in ischemic retinopathy, promoting glial activation, vascular inflammation, and injury. Reactive oxygen species (ROS), such as superoxide anion, interact with nitric oxide (NO) to form peroxynitrite, a potent reactive nitrogen species. Reactive nitrogen species (RNS) are highly reactive molecules derived from nitric oxide (NO), including peroxynitrite, nitrogen dioxide, and S-nitrosothiols. Formed during oxidative stress, RNS can modify proteins, lipids, and DNA, contributing to cellular injury. In diseases like DR, excess RNS promotes inflammation, endothelial dysfunction, and neurovascular damage. Peroxynitrite reacts with tyrosine residues in proteins, leading to the formation of nitrotyrosine, a stable biomarker of nitrosamine stress [28]. Nitrotyrosine accumulation contributes to DNA damage, protein dysfunction, and lipid peroxidation, which compromise cellular integrity and exacerbate oxidative damage (Fig. 2) [29]. These processes disrupt the blood-optic nerve barrier, intensifying retinal damage, particularly in ischemic and diabetic conditions. Nitrotyrosine, a marker of nitro-oxidative stress, is elevated in vitreous samples from diabetic retinopathy patients. Its levels correlate with disease severity and inflammation, making it a promising biomarker for assessing oxidative damage and monitoring therapeutic responses [28, 29].
Additionally, NOX-derived ROS are pivotal in sustaining chronic inflammation, as they amplify cytokine release and glial activation. This creates a feedforward loop that perpetuates tissue injury and impairs vascular repair mechanisms in the retina [29]. Targeting NOX isoforms and modulating nitro-oxidative stress pathways offer promising therapeutic opportunities for retinal diseases characterized by ischemia and neurovascular damage.
2.3. Role of NOS in Diabetic Retinopathy
Diabetes mellitus is associated with retinal vascular complications, driven by elevated oxidative stress and impaired NOS-mediated vasodilation [30]. The precise molecular mechanisms remain poorly understood, and the effect of diabetes on COX-mediated vasodilation is yet to be elucidated. DR is characterized by neuronal dysfunction and the breakdown of retinal vasculature, including alterations in vessel diameter regulation and oxygenation [31]. As we described earlier, NO plays a crucial role in maintaining vascular homeostasis by mediating vasodilation and regulating retinal blood flow. However, under pathological conditions, impaired NO production by eNOS and nNOS or excessive NO generation by iNOS disrupts this balance, leading to vascular complications and retinal damage.
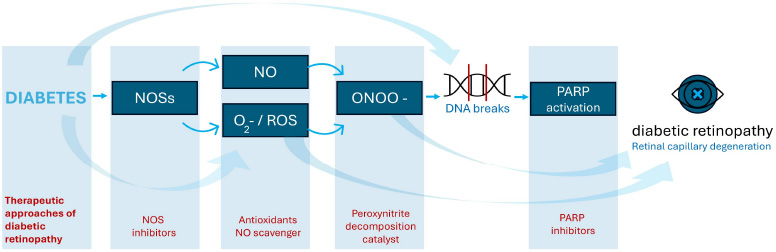
The role of oxidative and nitrosative stress in the development of diabetic retinopathy. O2= superoxide; NOS = nitric oxide synthase; ROS = reactive oxygen species; ONOO = peroxynitrite.
Nitro-oxidative stress and hyperglycaemia are key drivers of abnormal retinal microvascular changes [32]. Reduced NO bioavailability and increased peroxynitrite production lead to protein nitration, lipid peroxidation, and DNA damage, ultimately inducing tissue and cellular injury (Fig. 2) [33]. Notably, eNOS uncoupling, caused by BH4 depletion, shifts the enzyme from NO production to generating ROS, further exacerbating oxidative stress, making BH4 a potential therapeutic target [34]. Studies showed that human and murine retinal cells exposed to high glucose levels exhibit increased NOS isoform expression (especially iNOS), elevated NO levels, and heightened oxidative/nitrosamine stress compared to normoglycemic conditions [11, 35, 36]. This contributes to leukostasis, heightened vascular permeability, and neovascularization in DR. Additionally, NOX enzymes exacerbate nitro-oxidative stress by promoting vascular permeability and pathological angiogenesis, highlighting their role in DR pathogenesis.
NADPH oxidase (NOX) enzymes also play a crucial role in the formation of advanced glycation end-products (AGEs), significantly contributing to the pathogenesis of diabetic retinopathy [37]. Chronic hyperglycaemia stimulates NOX activity, resulting in excessive ROS production. These ROS accelerate the glycation of proteins and lipids, leading to the formation of AGEs, which disrupt retinal function and homeostasis [37]. AGEs impair endothelial cell integrity, increasing vascular permeability and contributing to diabetic macular edema. Furthermore, AGEs bind to their receptor, activating signaling pathways that promote inflammation, oxidative stress, and the upregulation of VEGF, thereby driving neovascularization. This feedforward cycle exacerbates retinal damage and dysfunction. The pivotal role of NOX enzymes in ROS generation and AGE formation underscores their potential as therapeutic targets for mitigating the progression of diabetic retinopathy [38, 39].
Two studies investigated the role of iNOS in early DR using iNOS knockout mice with streptozotocin (STZ)-induced diabetes [40]. Diabetic wild-type mice exhibited significant retinal abnormalities, including thinning of the retina, elevated NO levels, increased nitrated proteins, superoxide production, and leukostasis, compared to non-diabetic controls. They also showed a higher prevalence of acellular capillaries and pericyte ghosts, hallmarks of microvascular damage in DR. These pathological changes were largely prevented in iNOS knockout mice, indicating a protective effect of iNOS deletion. However, iNOS deficiency had no discernible impact on the function of the ganglion cell layer, suggesting that the protective role of iNOS deletion in DR is specific to microvascular pathology and does not extend to all aspects of retinal dysfunction.
The association between nNOS and DR has been extensively studied. Early evidence of neuronal dysfunction was observed in diabetic rats and human retinas, with aberrant electroretinogram (ERG) responses occurring before any detectable vascular damage [41, 42]. Additionally, increased retinal neuron apoptosis was identified as an early event in DR, preceding vascular damage in both rodent models and human cases [43]. Giove et al. investigated the role of nNOS in early DR by examining its expression and activity in retinal neurons [44]. The study revealed a strong anatomical correlation between increased NO production and nNOS immunoreactivity in the retinal plexiform layers of diabetic retinas. Although nNOS mRNA levels remained unchanged, nNOS protein levels decreased, accompanied by alterations in its subcellular localization. These findings indicate that heightened nNOS activity contributes to NO overproduction in retinal neurons, playing a significant role in the early neuronal dysfunction observed in DR.
The association between eNOS gene polymorphisms and an increased risk of DR has been widely discussed in the literature [45, 46]. Polymorphisms in the eNOS gene, which affect NO production, can impair endothelial function, leading to disrupted retinal blood flow and elevated oxidative stress. These genetic variations contribute to microvascular damage, inflammation, and neovascularization, exacerbating DR progression. Shi et al. demonstrated that the eNOS 4a/b polymorphism is a significant risk factor for DR in patients with type 2 diabetes [45]. This polymorphism may serve as a biomarker for early screening and diagnosis of DR, particularly in specific populations. The eNOS 4a/b polymorphism does not appear to increase the overall risk of DR in the general population, including Asians and Chinese patients, but the 4a allele specifically increases DR risk in Caucasians.
Additionally, this polymorphism does not influence the DR subtype. The rs1799983 GT genotype has been identified as an independent risk factor for DR in Greek patients, whereas the rs2070744 polymorphism showed no significant association [46]. Taverna et al. highlighted the impact of T-786C and C774T eNOS polymorphisms on DR onset patterns in Caucasians with type 1 diabetes [47]. The T-786C variant was associated with early-onset DR in patients with poor glycaemic control, while C774T correlated with late-onset DR, emphasizing the role of genetic factors in DR progression. Additionally, VEGF polymorphisms have been identified as DR risk factors, whereas NOS2A polymorphisms have been shown to provide a protective effect against DR [48]. Cheema et al. also demonstrated that specific eNOS gene polymorphisms offer protective effects against DR in Asian Indian populations [49].
eNOS is critical for maintaining vascular integrity in DR [50]. Diabetic eNOS-deficient mice exhibited a broader spectrum of retinal vascular complications compared to age-matched controls, including increased vascular leakage, indicative of compromised blood-retinal barrier integrity, and gliosis, reflecting elevated glial activation and retinitis [50]. The absence of eNOS likely impairs NO production, which is essential for vascular homeostasis, leading to oxidative stress and inflammation that exacerbate these pathological changes. These results emphasize the protective role of eNOS in preventing retinal vascular complications in diabetic conditions. Endothelial dysfunction, characterized by impaired release of vasodilators and vasoconstrictors, is a central contributor to DR. Connell et al. investigated the impact of hyperglycaemia on eNOS expression and NO release in bovine retinal endothelial cells under static and flow conditions [51]. Hyperglycaemia significantly reduced eNOS expression and NO release, with dose-dependent decreases observed in glucose-treated cells compared to osmotic controls. Furthermore, both acetylcholine-stimulated NO release and flow-induced NO activity were markedly inhibited by glucose. These findings highlight the role of hyperglycaemia in disrupting NO-mediated vascular regulation, leading to endothelial dysfunction and impaired vascular autoregulation—key features in the progression of DR.
The role of inducible iNOS and the bradykinin type 1 receptor (B1R) in DR was investigated by Othman et al. [52]. Their study demonstrated the significant contributions of iNOS and B1R to inflammation, oxidative stress, and vascular dysfunction in the diabetic retina. Using a streptozotocin-induced diabetes rat model, they showed that a selective iNOS inhibitor effectively reversed the increased expression of inflammatory markers, reduced vascular permeability, and disrupted the localization of iNOS and B1R. These findings suggest a mutual amplification loop between iNOS and B1R, identifying the B1R–iNOS axis as a promising therapeutic target for early intervention in DR.
The role of free radicals and NO dysregulation in DR has been extensively studied. Abu El-Asrar et al. demonstrated that increased NO production by inducible NOS contributes to neurotoxicity and angiogenesis in DR [53]. Additionally, Abu El-Asrar et al. identified the Stem Cell Factor (SCF)-c-kit signaling pathway as a driver of neovascularization in DR, highlighting increased expression of SCF, c-kit, eNOS, and VEGF as key contributors to angiogenesis and oxidative damage in disease progression [54]. Further clinical studies corroborate the association between oxidative stress and DR severity. Elevated NO levels in the aqueous humor, increased lipid peroxidation, and mitochondrial dysfunction have also been observed in DR patients, providing additional evidence of oxidative damage in disease pathogenesis [55-57]. These findings emphasize the pivotal role of oxidative stress and NO dysregulation in DR progression, highlighting potential therapeutic targets.
2.4. The Association of Oxidative Stress and Neurodegeneration in DR
Neurodegeneration in DR is intricately linked to oxidative stress, which emerges as a primary pathological mechanism triggered by chronic hyperglycemia [58]. In the diabetic state, elevated glucose metabolism leads to excessive production of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and reactive nitrogen species (RNS), surpassing the retina’s natural antioxidant defense systems. This oxidative imbalance leads to significant damage to retinal neurons, particularly ganglion and intraneuronal cells, through lipid peroxidation, DNA fragmentation, and mitochondrial dysfunction [59]. Furthermore, oxidative stress promotes the activation of inflammatory pathways and retinal glial cells, aggravating neuronal loss and disrupting the neurovascular unit. Neurodegeneration and inflammation are thus critical early events in the pathogenesis of DR. Experimental studies and clinical evidence underscore the need for early intervention targeting oxidative damage [60]. Promising neuroprotective strategies include combination therapies, such as citicoline with resveratrol, duloxetine with N-acetylcysteine, and angiopoietin-2 inhibitors with CD5-2 [58]. These approaches aim to preserve retinal structure and function in early DR and may offer new avenues for delaying disease progression and preventing vision loss.
2.5. Therapeutic Targets of NOS in DR
Early diagnosis and effective treatment can delay the onset and progression of DR [61]. Therapeutic strategies targeting NOS isoforms often involve modulating their activity through the supplementation of cofactors or reducing oxidative stress. However, studies indicate that chronic administration of L-arginine, the primary substrate for NOS, does not consistently enhance NO production or improve endothelial function [5]. Instead, prolonged L-arginine supplementation increases urea and L-ornithine levels without significantly promoting NO synthesis (Fig. 1). While short-term L-arginine supplementation improves vascular reactivity in peripheral arterial disease (PAD), Wilson et al. reported no such benefits with long-term administration [62]. Arginase competes with NOS for L-arginine, limiting NO production and promoting NOS uncoupling, where NOS generates superoxide anions instead of NO. Targeting arginase activity has been proposed as a therapeutic strategy to mitigate oxidative stress and restore NO balance. Blockade of vascular arginase may improve endothelial function in retinal arterioles during the early stages of diabetes [63]. A study in diabetic pig coronary arterioles demonstrated that impaired NO-mediated vasodilation was restored by the arginase inhibitor (nor-NOHA) or L-arginine. Nor-NOHA blocks arginase, ensuring L-arginine availability for eNOS and preserving NO production [64].
Hyperglycaemia significantly increases retinal arginase activity and arginase 1 expression in diabetic microvascular endothelial cells [65]. Elevated arginase 2 levels during the ischemic phase of oxygen-induced retinopathy (OIR) coincide with increased nitro-oxidative stress, iNOS expression, impaired vascular repair, and vitreoretinal neovascularization. Deletion of arginase 2 mitigated these adverse effects, highlighting its therapeutic potential [66]. Shosha et al. highlighted the critical role of arginase 2 (A2) in neurovascular injury following retinal ischemia in DR [67]. Using A2-deficient and wild-type (WT) mice, they demonstrated that ischemic insult significantly increased A2 expression in WT retinas. Deletion of A2 markedly reduced ganglion cell loss and ROS production. A2 deficiency also preserved retinal morphology and improved retinal function, as confirmed by electroretinography. These findings suggest that A2 mediates neurovascular damage in ischemic retinas, identifying A2 as a promising therapeutic target for mitigating retinal neurovascular injury.
Additionally, Edgar et al. demonstrated that sepiapterin, a precursor of tetrahydrobiopterin (BH4), increased BH4 levels in Hyperoxia-exposed retinas, thereby enhancing NOS activity. BH4 supplementation was shown to restore retinal microvascular endothelial cell function and improve vascular integrity by optimizing eNOS activity. These findings emphasize the therapeutic potential of BH4 in maintaining endothelial function and mitigating retinal vascular damage [20].
Resveratrol is a promising therapeutic agent known to reduce oxidative stress and enhance eNOS expression [68]. It has been shown to upregulate eNOS in vascular endothelial cells, supporting vascular homeostasis. Furthermore, resveratrol protects against ischemia-induced retinal ganglion cell loss and endothelial dysfunction in murine retinas by mitigating nitro-oxidative stress, likely through the suppression of NOX2 upregulation [69].
Betulinic acid has shown promising therapeutic effects in addressing ischemic retinal damage associated with DR [70]. In a study, Betulinic acid (50 mg/kg/day) administered to rat models significantly preserved retinal ganglion cells and optic nerve axons compared to untreated controls. Additionally, it reduced ROS levels, improved vascular endothelial function, and enhanced the expression of antioxidant enzymes. These findings suggest that Betulinic acid protects against ischemic retinal injury in DR by mitigating oxidative stress and improving vascular function.
NOX inhibitors are emerging as promising therapeutic agents for mitigating ischemic and diabetic retinopathy due to their critical role in reducing excessive ROS production, a key factor in these conditions. Synthetic NOX inhibitors, such as GKT1 are potent, orally active, and bioavailable, specifically targeting NOX isoforms [71, 72]. These compounds have been shown to significantly lower ROS production and VEGF-An expression in human retinal endothelial cells exposed to dimethyloxalylglycine [73]. NCT04569656 also investigated GKT137831, a NOX1/4 inhibitor, for its anti-inflammatory effects in ischemic retinopathies, such as diabetic retinopathy. In a rat model, GKT137831 reduced leukocyte adhesion, glial activation, vascular leakage, and the expression of inflammatory markers, including VEGF and MCP-1. In vitro, it suppressed the expression of ROS and cytokines in retinal microglia, Müller cells, and neurons under hypoxic conditions. These findings suggest GKT137831 may protect against retinal inflammation and oxidative damage, supporting its potential as a therapeutic option for vision-threatening retinopathies.
Another therapeutic avenue in retinal microvascular disorders involves the endocannabinoid system [74]. The cannabinoid receptor CB2 plays a pivotal role in immune regulation, although its neuronal expression in the retina remains uncertain. CB2 expression in healthy retinas is minimal but upregulated under pathological conditions. CB2 knockout mice exhibited increased a-wave responses and altered bipolar cell activity, as observed through electroretinogram recordings [74, 75]. Lipidomics analyses in these knockout mice revealed modest reductions in cannabinoid-related lipids, suggesting that CB2 may influence retinal signaling indirectly, with its upregulation primarily associated with DR.
The therapeutic potential of exendin-4, a glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptor agonist, has also been explored in DR. Exendin-4 restores microvascular patency in ischemic DR through the GLP-1 receptor–eNOS signaling pathway, enhancing endothelial NO production, vasodilation, and blood flow regulation [76]. This highlights its promise in improving tissue perfusion and regulating retinal capillary function.
Natural compounds, such as ginger and naringenin, have demonstrated significant potential in managing DR and high glucose-induced ischemic injury [77, 78]. Ginger, rich in bioactive phytochemicals like gingerol and shogaol, exhibits antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and hypoglycaemic properties. In type 2 diabetic rats, ginger extract improved glucose and lipid profiles, insulin sensitivity, and oxidative and inflammatory markers while reducing oxidative damage, angiogenesis, and apoptosis [77]. It also enhanced the expression of eNOS and G6PDH. Similarly, naringenin, a flavonoid, protected retinal endothelial cells from high glucose-induced injury by reducing ROS levels, inhibiting apoptosis, and promoting the release of BH4 [78]. Both compounds represent cost-effective therapeutic strategies for addressing diabetic retinal complications.
CONCLUSION
DR is a complex retinal disorder driven by oxidative stress, nitro-oxidative imbalance, and endothelial dysfunction, and exacerbated by hyperglycemia. The role of NO and its synthases (NOS isoforms) is central to retinal vascular regulation, with disruptions contributing to retinal damage. Emerging evidence highlights the therapeutic potential of targeting pathways, including NOS modulation, BH4 supplementation, and arginase inhibition, to restore vascular homeostasis. Innovative treatments, including NOX inhibitors, resveratrol, and betulinic acid, have demonstrated efficacy in reducing oxidative stress and vascular injury. Additionally, natural compounds like ginger and naringenin offer cost-effective strategies for mitigating DR progression. These findings highlight the significance of multifaceted therapeutic approaches for managing DR.
AUTHORS' CONTRIBUTIONS
The authors confirm their contributions to the paper as follows: L.E.: Study conception and design; L.T.I, D.S.M. and A.M.A.: Draft manuscript. All authors reviewed the results and approved the final version of the manuscript.
LIST OF ABBREVIATIONS
| AGEs | = Advanced Glycation End Products |
| BH4 | = Tetrahydrobiopterin |
| B1R | = Bradykinin Type 1 Receptor |
| CB2 | = Cannabinoid Receptor Type 2 |
| COX | = Cyclooxygenase |
| cGMP | = Cyclic Guanosine Monophosphate |
| DR | = Diabetic Retinopathy |
| eNOS | = Endothelial Nitric Oxide Synthase |
| ERG | = Electroretinogram |
| GLP-1 | = Glucagon-like Peptide-1 |
| iNOS | = Inducible Nitric Oxide Synthase |
| mRNA | = Messenger Ribonucleic Acid |
| nNOS | = Neuronal Nitric Oxide Synthase |
| NO | = Nitric Oxide |
| NOX | = NADPH Oxidase |
| NOS | = Nitric Oxide Synthase |
| OIR | = Oxygen-Induced Retinopathy |
| PAD | = Peripheral Arterial Disease |
| PGI2 | = Prostacyclin |
| RNS | = Reactive Nitrogen Species |
| ROS | = Reactive Oxygen Species |
| sGC | = Soluble Guanylate Cyclase |
| STZ | = Streptozotocin |
| VEGF | = Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor |
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
Declared none.


